Page 1 of 1
Tutorial on AT Commands for GSM/GPRS with microcontrollers
Posted: Wed Sep 26, 2012 3:30 am
by SevenZero
AT commands are used to control MODEMs. AT is the abbreviation for Attention. These commands come from Hayes commands that were used by the Hayes smart modems. The Hayes commands started with AT to indicate the attention from the MODEM. The dial up and wireless MODEMs (devices that involve machine to machine communication) need AT commands to interact with a computer. These include the Hayes command set as a subset, along with other extended AT commands.
If you use a GSM/GPRS module such as
SIM900, you will need to use these commands.
AT commands with a GSM/GPRS MODEM or mobile phone can be used to access following information and services:
Information and configuration pertaining to mobile device or MODEM and SIM card.
- SMS services
- MMS services
- Fax services
- Data and Voice link over mobile network
The Hayes subset commands are called the basic commands and the commands specific to a GSM network are called extended AT commands.
Types of AT Commands
There are four types of AT commands as below.
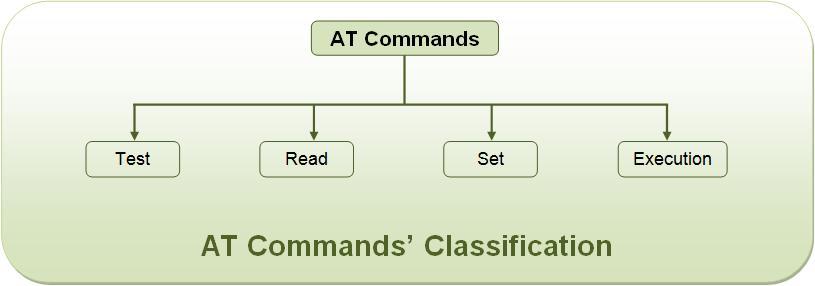
- AT.jpg (16.28 KiB) Viewed 22872 times
- Test commands - used to check whether a command is supported or not by the MODEM.
SYNTAX: AT<command name>=?
For example: ATD=?
- Read command - used to get mobile phone or MODEM settings for an operation.
SYNTAX: AT<command name>?
For example: AT+CBC?
- Set commands - used to modify mobile phone or MODEM settings for an operation.
SYNTAX: AT<command name>=value1, value2, …, valueN
Some values in set commands can be optional.
For example: AT+CSCA=”+9876543210”, 120
- Execution commands - used to carry out an operation.
SYNTAX: AT<command name>=parameter1, parameter2, …, parameterN
The read commands are not available to get value of last parameter assigned in execution commands because parameters of execution commands are not stored.
For example: AT+CMSS=1,”+ 9876543210”, 120
Commonly used AT commands in detail
Explanation of commonly used AT commands:
- AT - This command is used to check communication between the module and the computer.
For example,
AT
OK
The command returns a result code OK if the computer (serial port) and module are connected properly. If any of module or SIM is not working, it would return a result code ERROR.
- +CMGF - This command is used to set the SMS mode. Either text or PDU mode can be selected by assigning 1 or 0 in the command.
SYNTAX: AT+CMGF=<mode>
0: for PDU mode
1: for text mode
The text mode of SMS is easier to operate but it allows limited features of SMS. The PDU (protocol data unit) allows more access to SMS services but the operator requires bit level knowledge of TPDUs. The headers and body of SMS are accessed in hex format in PDU mode so it allows availing more features.
For example,
AT+CMGF=1
OK
- +CMGW - This command is used to store message in the SIM.
SYNTAX: AT+CMGW=” Phone number”> Message to be stored Ctrl+z
As one types AT+CMGW and phone number, ‘>’ sign appears on next line where one can type the message. Multiple line messages can be typed in this case. This is why the message is terminated by providing a ‘Ctrl+z’ combination. As Ctrl+z is pressed, the following information response is displayed on the screen.
+CMGW: Number on which message has been stored
- +CMGS - This command is used to send a SMS message to a phone number.
SYNTAX: AT+CMGS= serial number of message to be send.
As the command AT+CMGS and serial number of message are entered, SMS is sent to the particular SIM.
For example,
AT+CMGS=1
OK
- ATD - This command is used to dial or call a number.
SYNTAX: ATD<Phone number>(Enter)
For example,
ATD123456789
- ATA - This command is used to answer a call. An incoming call is indicated by a message ‘RING’ which is repeated for every ring of the call. When the call ends ‘NO CARRIER’ is displayed on the screen.
SYNTAX: ATA(Enter)
As ATA followed by enter key is pressed, incoming call is answered.
For example,
RING
RING
ATA
- ATH - This command is used to disconnect remote user link with the GSM module.
SYNTAX: ATH (Enter)
List of AT commands
The AT commands for both, GSM module and the mobile phone, are listed below. Some of these commands may not be supported by all the GSM modules available. Also there might be some commands which won’t be supported by some mobile handsets.
| Testing |
| Command | Description |
| AT | Checking communication between the module and computer |
| Call control |
| Command | Description |
| ATA | Answer command |
| ATD | Dial command |
| ATH | Hang up call |
| ATL | Monitor speaker loudness |
| ATM | Monitor speaker mode |
| ATO | Go on-line |
| ATP | Set pulse dial as default |
| ATT | Set tone dial as default |
| AT+CSTA | Select type of address |
| AT+CRC | Cellular result codes |
| Data card Control |
| Command | Description |
| ATI | Identification |
| ATS | Select an S-register |
| ATZ | Recall stored profile |
| AT&F | Restore factory settings |
| AT&V | View active configuration |
| AT&W | Store parameters in given profile |
| AT&Y | Select Set as power up option |
| AT+CLCK | Facility lock command |
| AT+COLP | Connected line identification presentation |
| AT+GCAP | Request complete capabilities list |
| AT+GMI | Request manufacturer identification |
| AT+GMM | Request model identification |
| AT+GMR | Request revision identification |
| AT+GSN | Request product serial number identification (IMEI) |
| Phone control |
| Command | Description |
| AT+CBC | Battery charge |
| AT+CGMI | Request manufacturer identification |
| AT+CGMM | Request model identification |
| AT+CGMR | Request revision identification |
| AT+CGSN | Request product serial number identification |
| AT+CMEE | Report mobile equipment error |
| AT+CPAS | Phone activity status |
| AT+CPBF | Find phone book entries |
| AT+CPBR | Read phone book entry |
| AT+CPBS | Select phone book memory storage |
| AT+CPBW | Write phone book entry |
| AT+CSCS | Select TE character set |
| AT+CSQ | Signal quality |
| Computer data interface |
| Command | Description |
| ATE | Command Echo |
| ATQ | Result code suppression |
| ATV | Define response format |
| ATX | Response range selection |
| AT&C | Define DCD usage |
| AT&D | Define DTR usage |
| AT&K | Select flow control |
| AT&Q | Define communications mode option |
| AT&S | Define DSR option |
| AT+ICF | DTE-DCE character framing |
| AT+IFC | DTE-DCE Local flow control |
| AT+IPR | Fixed DTE rate |
| Service |
| Command | Description |
| AT+CLIP | Calling line identification presentation |
| AT+CR | Service reporting control |
| AT+DR | Data compression reporting |
| AT+ILRR | DTE-DCE local rate reporting |
| Network Communication parameter |
| Command | Description |
| ATB | Communications standard option |
| AT+CBST | Select bearer service type |
| AT+CEER | Extended error report |
| AT+CRLP | Radio link protocol |
| AT+DS | Data compression |
| Miscellaneous |
| Command | Description |
| A/ | Re-execute command line |
| AT? | Command help |
| AT*C | Start SMS interpreter |
| AT*T | Enter SMS block mode protocol |
| AT*V | Activate V.25bis mode |
| AT*NOKIATEST | Test command |
| AT+CESP | Enter SMS block mode protocol |
| SMS Text mode |
| Command | Description |
| AT+CSMS | Select message service |
| AT+CPMS | Preferred message storage |
| AT+CMGF | Message format |
| AT+CSCA | Service centre address |
| AT+CSMP | Set text mode parameters |
| AT+CSDH | Show text mode parameters |
| AT+CSCB | Select cell broadcast message types |
| AT+CSAS | Save settings |
| AT+CRES | Restore settings |
| AT+CNMI | New message indications to TE |
| AT+CMGL | List messages |
| AT+CMGR | Read message |
| AT+CMGS | Send message |
| AT+CMSS | Send message from storage |
| AT+CMGW | Write message to memory |
| AT+CMGD | Delete message |
| SMS PDU mode |
| Command | Description |
| AT+CMGL | List Messages |
| AT+CMGR | Read message |
| AT+CMGS | Send message |
| AT+CMGW | Write message to memory |
Re: Tutorial on AT Commands for GSM/GPRS with microcontrollers
Posted: Wed Sep 26, 2012 11:38 am
by SevenZero
Here are some objectives that are fulfilled using AT Commands:
- Test the simple AT Command.
- Find out the IMEI number of the GSM Modem.
- Connect a call to a GSM mobile number (Dial a number).
- Send a text message to a mobile number.
AT Commands used to perform the above operations have been given below along with their output. (For complete list of AT Commands supported by GSM Modem, refer the list in tutorial on AT Commands.
- Test the simple AT Command
AT (Enter)
OK
- Find out the IMEI number of the GSM modem
AT+GSN (Enter)
xxxxxxxxxxxxxxx(15- digit unique IMEI number)
OK
- Dial a number
ATDXXXXXXXXXX; (Enter) (10-digit mobile number)
OK
- Send a text message.
AT+CMGS= “XXXXXXXXXX” (Enter) (10-digit mobile number)
>Hello ^z (Enter message after ‘>’ and use Ctrl+z to terminate the message)
Programming Steps:
- Store all AT commands into strings
- Set the baud rate of microcontroller to 9600bps
- Enable serial port. (Refer USART with PIC)
- Enable the global and peripheral interrupt bits of the INTCON register
- Configure Port D as input port
- Use if condition to detect the pressed switch
- As switch is pressed, process the corresponding AT command and transmit via USART
- Reception interrupt method is used to store the GSM output data into an array
- Display the stored value on the LCD. (Refer displaying text on LCD using PIC)
Re: Tutorial on AT Commands for GSM/GPRS with microcontrollers
Posted: Wed Sep 26, 2012 11:55 am
by SevenZero
Sample circuit diagram on connecting a GPRS module such as the ones you can find from
TRONIC.LK.
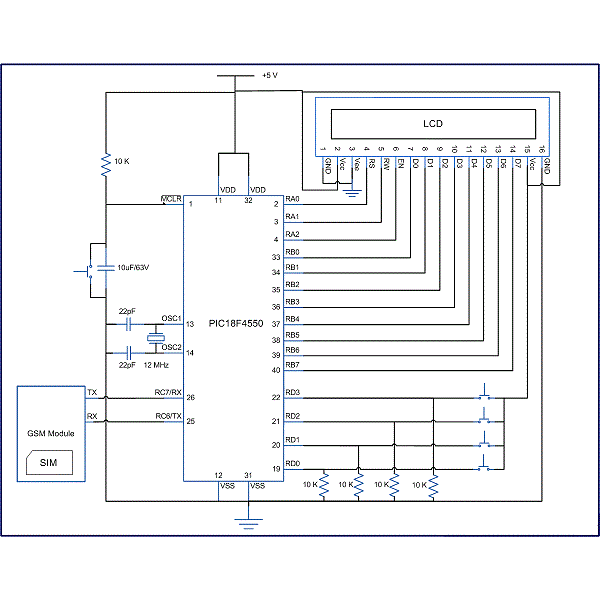
- GSM_CD.gif (21.89 KiB) Viewed 22856 times
Here is a sample code is C language:
Code: Select all
/*
This code takes four choices as four inputs
Choice 1 : Test the simple AT Command
Choice 2 : Find out the IMEI number of the GSM Modem
Choice 3 : Connect a call to a GSM mobile number
Choice 4 : Send a text message to a mobile number
*/
#define FREQ 12000000
#define baud 9600
#define spbrg_value (((FREQ/64)/baud)-1)
#define rs LATA.F0
#define rw LATA.F1
#define en LATA.F2
#define lcdport LATB
void tx_data(unsigned char);
unsigned char rx_data();
void lcd_ini();
void lcdcmd(unsigned char);
void lcddata(unsigned char);
void gsm_cmd(unsigned char *);
void output(void);
unsigned char value = 0;
int i=0,j,k,temp,flag,choice;
unsigned char *starting_text = "Enter choice=";
unsigned char *dial_text = "Dialing...";
unsigned char *at_cmd = "AT";
unsigned char *imei_cmd = "AT+GSN";
unsigned char *call_cmd = "ATD9xxxxxxxxx;"; // Provide a 10-Digit Mobile Number
unsigned char *sms_format = "AT+CMGF=1";
unsigned char *sms_write = "AT+CMGS=\"xxxxxxxxxx\""; // 10-Digit Mobile Number
unsigned char *sms = "Hello";
unsigned char *sms_report = "SMS Sent...";
unsigned char sms_terminate = 0x1A;
unsigned char enter = 0x0D;
unsigned char *data;
void main()
{
TRISB=0; // Set Port B as output port
LATB=0;
TRISA=0;
LATA=0;
TRISD=0xFF;
LATD=0;
SPBRG=spbrg_value; // Fill SPBRG register to set the baud rate
RCSTA.SPEN=1; // To activate serial port (Tx and Rx pins)
TXSTA.TXEN=1; // Activate Transmissiom
RCSTA.CREN=1; // Activate Reception
PIE1.RCIE=1; // Enable Reception interrupt
INTCON.GIE=1; // Enable Global interrupt
INTCON.PEIE=1; // Enable Peripheral interrupt
lcd_ini();
while(1)
{
k = 0;
lcdcmd(0x80);
while(starting_text[k]!='\0')
{
lcddata(starting_text[k]);
k++;
}
//Check inputs
//Choice 1
if(PORTD.F0)
{
gsm_cmd(at_cmd);
output();
Delay_ms(1000);
}
//Choice 2
if(PORTD.F1)
{
gsm_cmd(imei_cmd);
output();
Delay_ms(1000);
}
//Choice 3
if(PORTD.F2)
{
gsm_cmd(call_cmd);
output();
Delay_ms(1000);
}
//Choice 4
if(PORTD.F3)
{
gsm_cmd(sms_format);
output();
Delay_ms(1000);
gsm_cmd(sms_write);
output();
Delay_ms(1000);
gsm_cmd(sms);
output();
tx_data(0x1A);
Delay_ms(1000);
}
}
}
void gsm_cmd(unsigned char *string)
{
i=0;j=0;
while(string[i]!='\0')
{
temp=0;
if(string[i]==0x5C) // Not to send '\' cahracter
i++;
tx_data(string[i]); // Send by serial communication
i++;
while(temp!=1);
}
temp=0;
tx_data(enter); // Send ASCII code for 'Enter' key
while(temp!=1);
}
void output(void) // To print data on LCD
{
lcdcmd(0x01);
i=-1;flag=0;
while(i<j)
{
if(flag>1)
{
flag=0;
Delay_ms(500);
lcdcmd(0x01);
lcdcmd(0x80);
}
if(data[i]==0x0A) // This condition is to avoid double Enter
// during execution of a command
{
flag++;
lcdcmd(0xc0);
}
if(data[i]=='>'||data[i]=='"') // Not to print this character
{
i++;
lcdcmd(0xc0);
}
if(data[i]!=0x0D&&data[i]!=0x0A&&data[i]!=0x1A) // Condition to print the data
// except 'Enter','New line' and 'Submit'
{
lcddata(data[i]);
i++;
}
else
i++;
Delay_ms(300);
}
lcdcmd(0x01);
}
void tx_data(unsigned char serial_data) // Transmit data function
{
TXREG = serial_data;
while(PIR1.TXIF==0);
}
void interrupt()
{
data[j]=RCREG; // Store the data into array when Reception interrupt occurs
value=RCREG;
j++;
temp=1;
}
void lcd_ini()
{
lcdcmd(0x38); // Configure the LCD in 8-bit mode, 2 line and 5x7 font
lcdcmd(0x0C); // Display On and Cursor Off
lcdcmd(0x01); // Clear display screen
lcdcmd(0x06); // Increment cursor
lcdcmd(0x80); // Set cursor position to 1st line, 1st column
}
void lcdcmd(unsigned char cmdout)
{
lcdport=cmdout; //Send command to lcdport=PORTB
rs=0;
rw=0;
en=1;
Delay_ms(10);
en=0;
}
void lcddata(unsigned char dataout)
{
lcdport=dataout; //Send data to lcdport=PORTB
rs=1;
rw=0;
en=1;
Delay_ms(10);
en=0;
}
Re: Tutorial on AT Commands for GSM/GPRS with microcontrollers
Posted: Wed Sep 26, 2012 7:51 pm
by nipunalanka
this cct can use phone,not chip
Re: Tutorial on AT Commands for GSM/GPRS with microcontrollers
Posted: Wed Sep 26, 2012 9:22 pm
by nipunalanka
no i wont connect to nokia 1110 or 1100 phone friend
Re: Tutorial on AT Commands for GSM/GPRS with microcontrollers
Posted: Fri Sep 28, 2012 8:28 pm
by Neo
Nipuna, it is not possible to use AT commands with Nokia 1100 as there is no modem in there. But Nokia F-BUS protocol is there. But you need to use a different protocol to use that. Search for Nokia F-Bus.
Here are the connecters for f-bus.

- Nokia 1100_1.jpg (7.53 KiB) Viewed 22839 times

- Nokia 1100_2.jpg (5.58 KiB) Viewed 22839 times
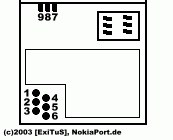
- Nokia 1100_3.gif (2.58 KiB) Viewed 22839 times
| PIN | DESCRIPTION |
| 1 | DAI CLK |
| 2 | F-Bus Rx |
| 3 | F-Bus Tx |
| 4 | Gnd |
| 5 | M-Bus |
| 6 | Vpp |
| 7 | Gnd |
| 8 | BSI |
| 9 | Vcc |
Here is the link for Nokia 1100 schematics.
http://www.cpkb.org/wiki/Nokia_1100_110 ... c_download
This link has some good information about F-BUS.
http://www.embedtronics.com/nokia/fbus.html
Re: Tutorial on AT Commands for GSM/GPRS with microcontrollers
Posted: Fri Mar 08, 2013 11:15 am
by maria752
Have you any idea about HTC mobile circuit.... i have found Mic problem but it is hard to task to compile the solution. according to your upper solution this become very beneficiary for me....